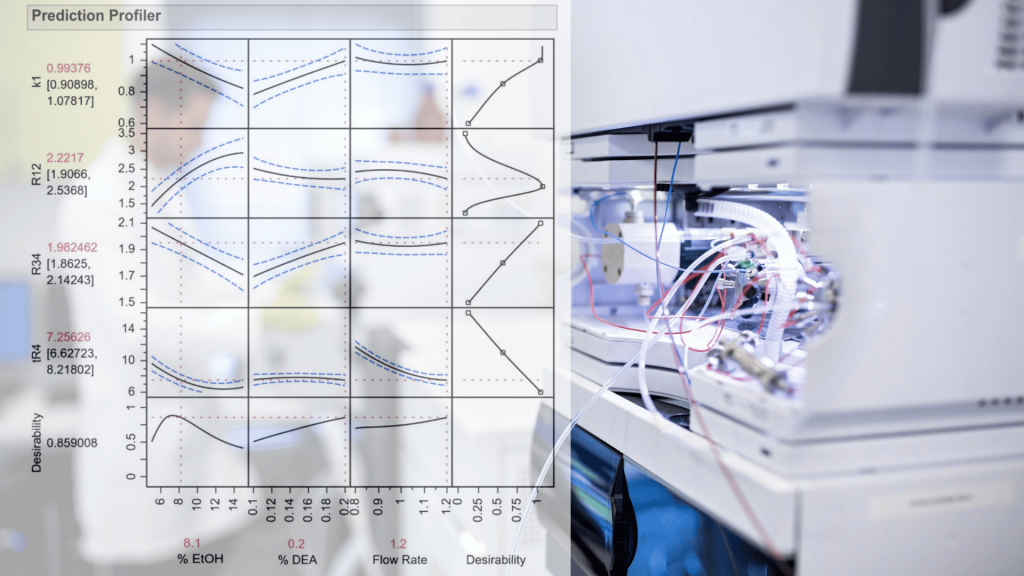
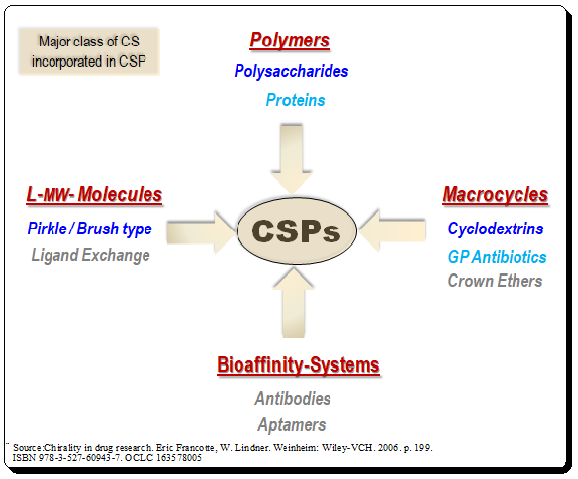
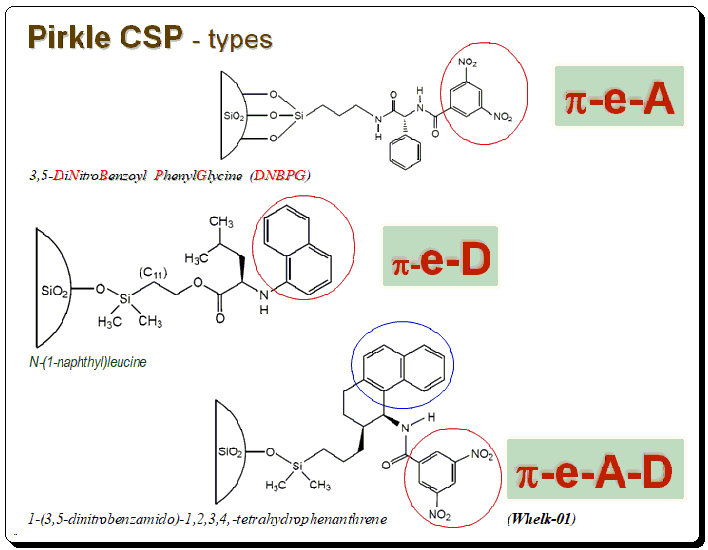
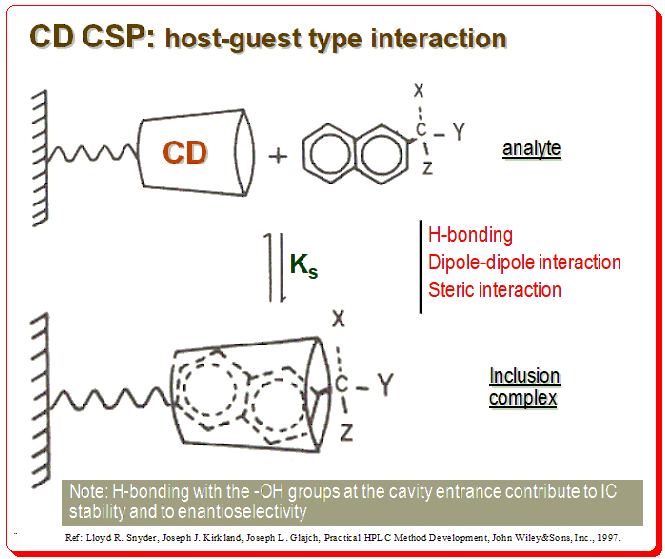
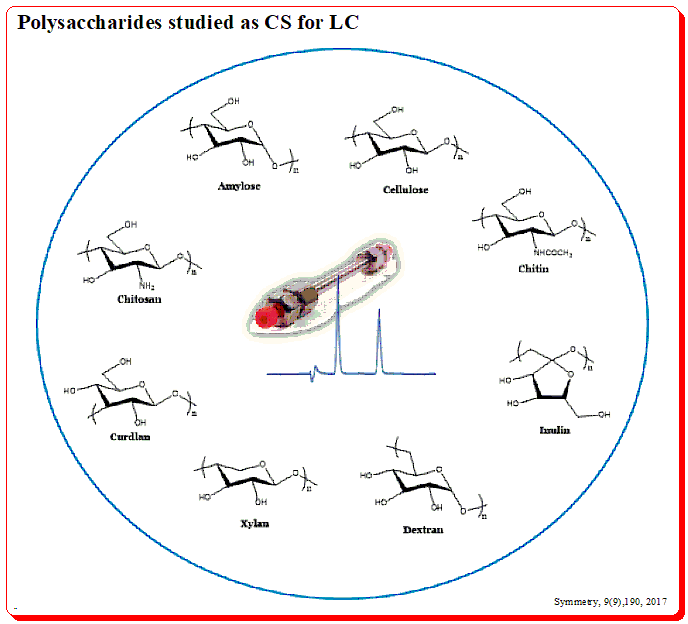
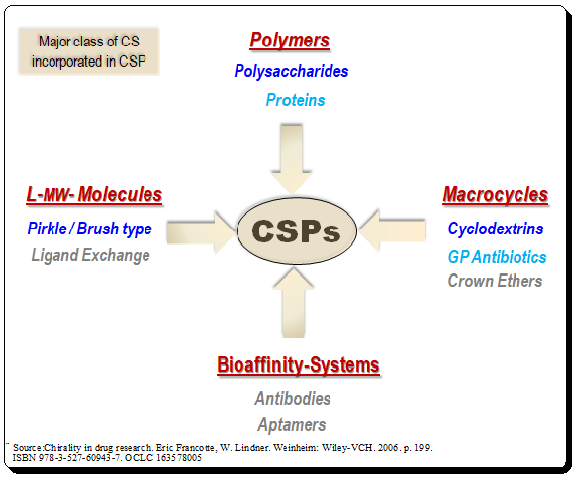
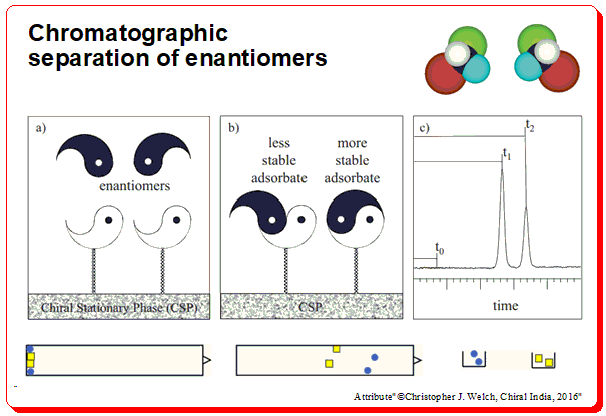
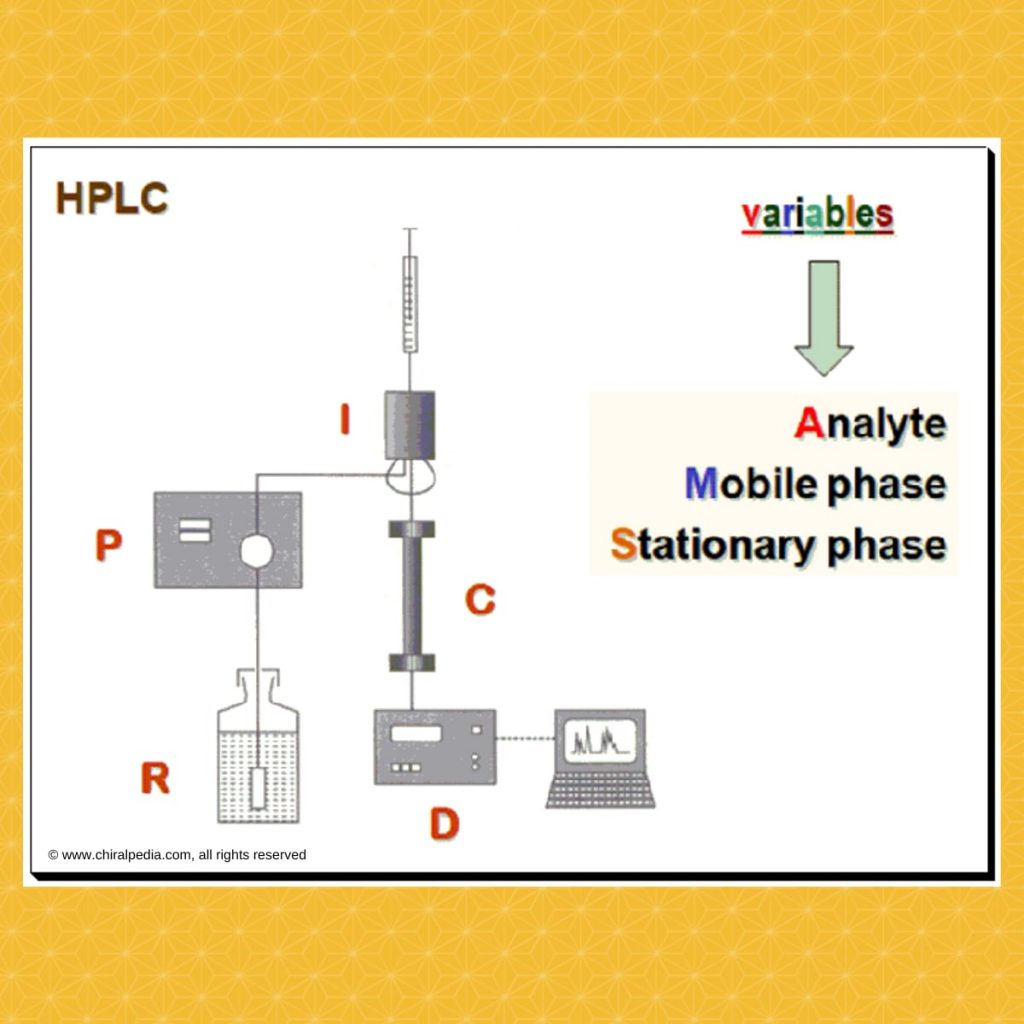
Harnessing JMP’s Prediction Profiler for Multi-Response Optimization of HPLC Method in Chiral Drug Separation
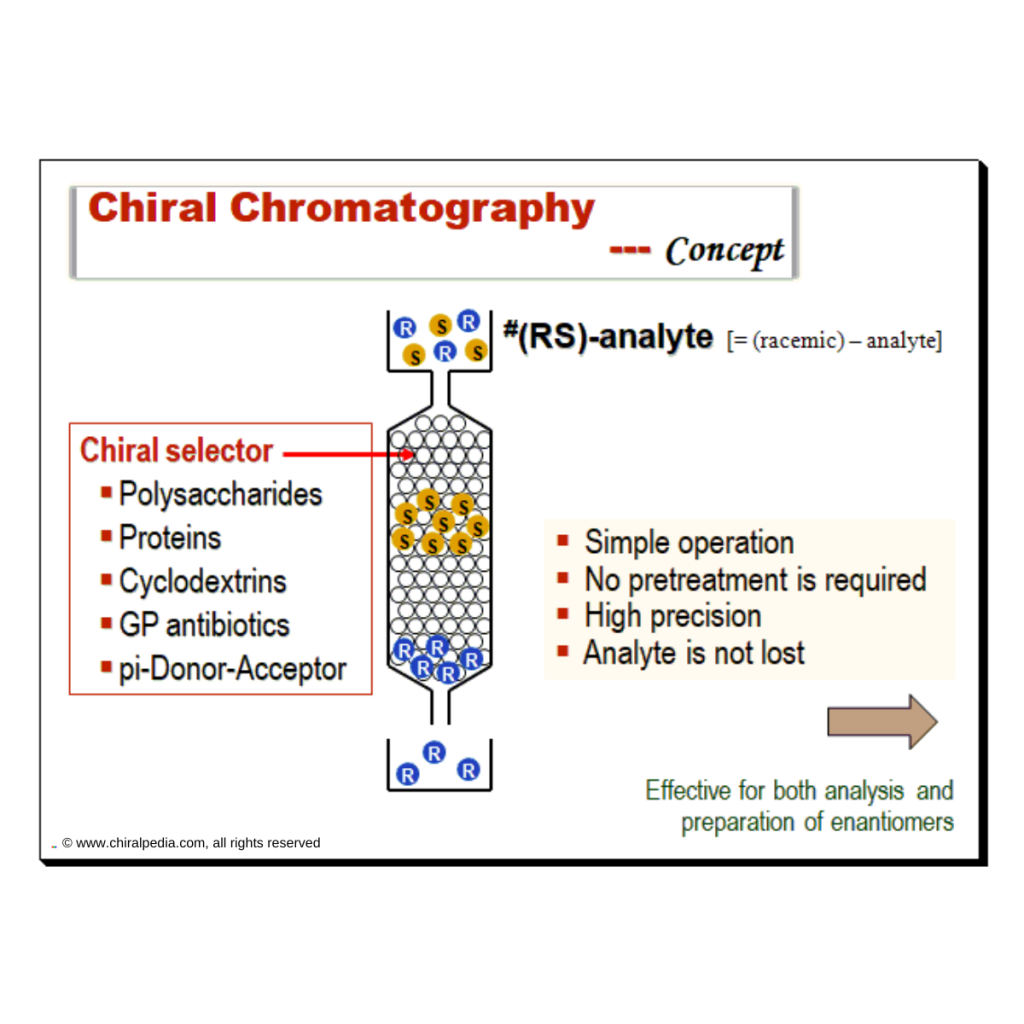
Synopsis The development of chromatographic methods for the separation of chiral drugs presents a significant challenge, necessitating a comprehensive understanding of the compounds’ chemical properties and the factors influencing their separation. This task is further complicated by the presence of process-related impurities that can disrupt the separation process and compromise the quality of the results. However, the application of advanced statistical tools such as JMP’s Design of Experiments (DoE) and Prediction Profiler can significantly streamline …