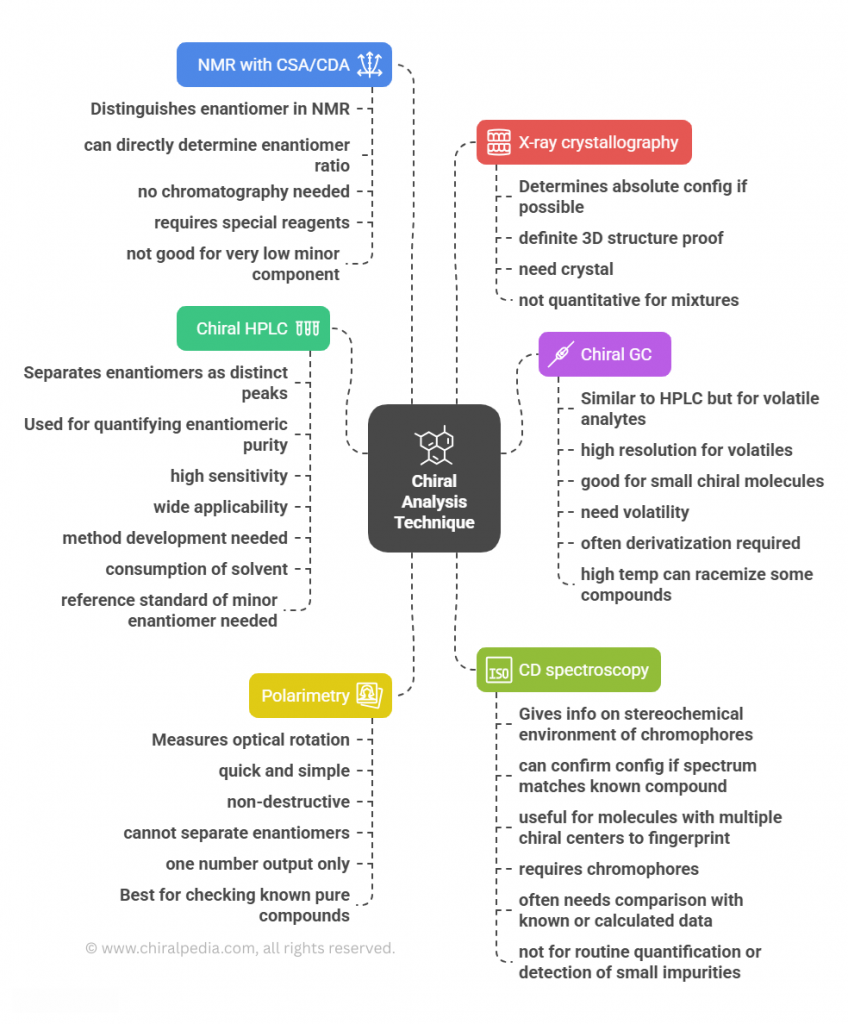
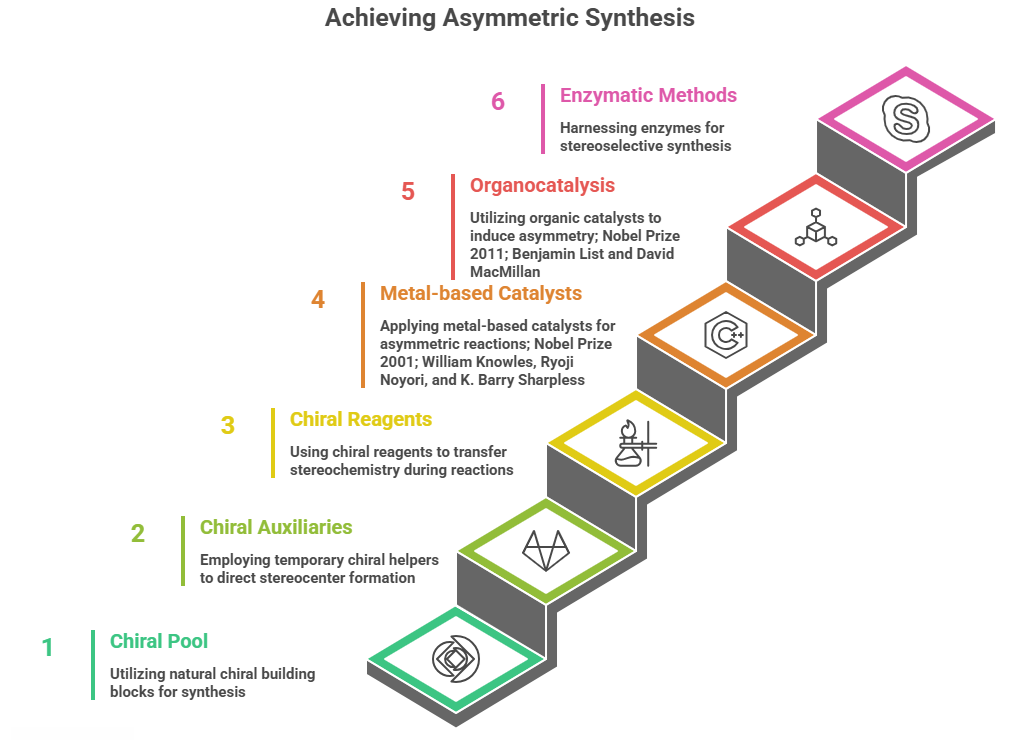
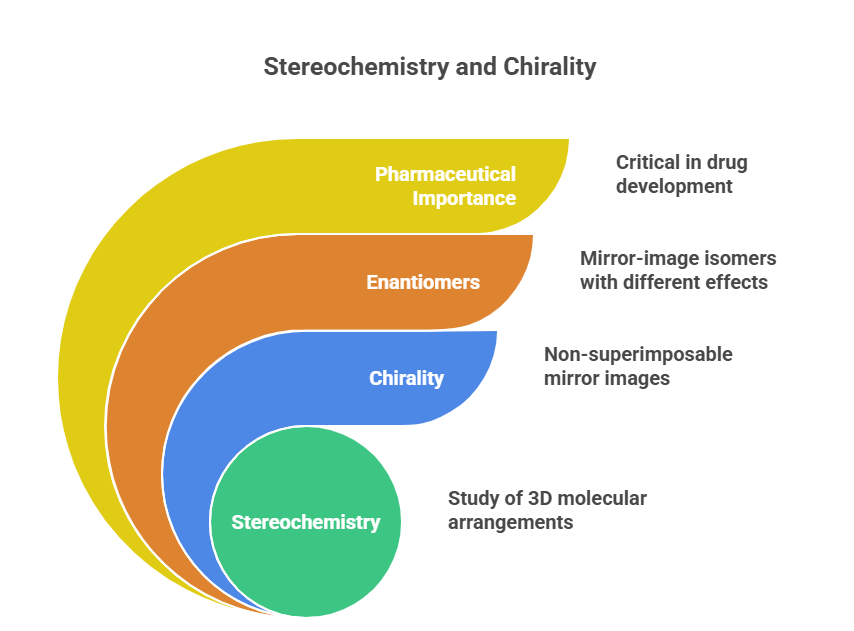
The Hidden Chirality in Drug Metabolites: A metabolic blind spot
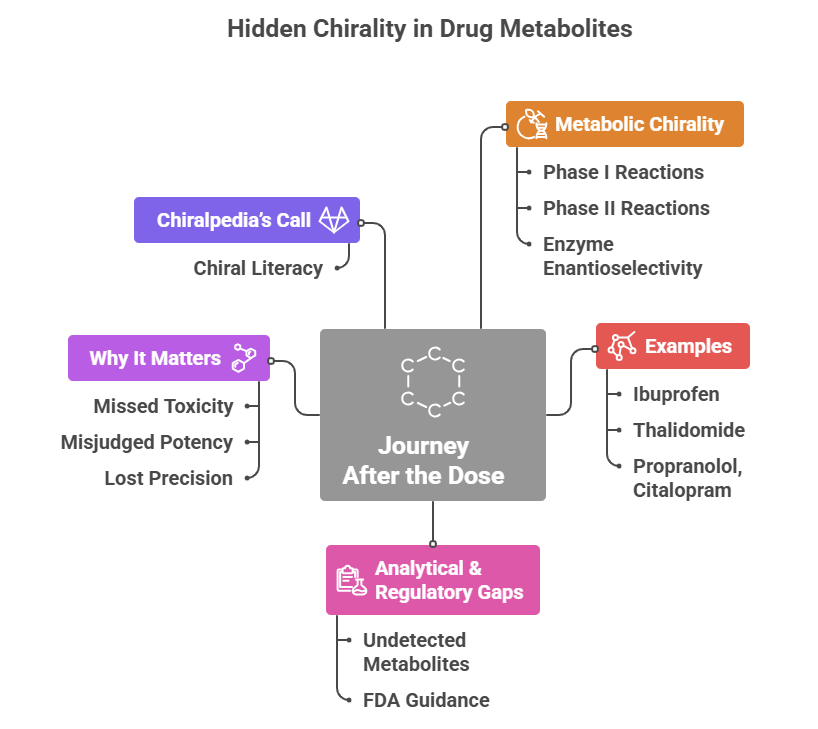
“Chirality isn’t hidden — we just stopped looking closely enough” The Unseen Journey After the Dose: 💊 When a patient swallows a drug, the journey is far from over. Sometimes, the real chiral story begins after the dose. The drug molecule meets a series of enzymes — oxidases, reductases, transferases — each capable of transforming it into one or more metabolites. We often assume these are simply inactive breakdown products, but chemistry rarely plays it …
The Hidden Chirality in Drug Metabolites: A metabolic blind spot Read More »