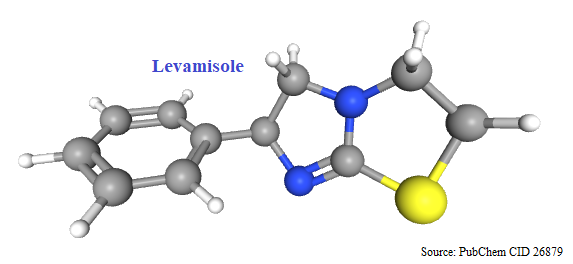
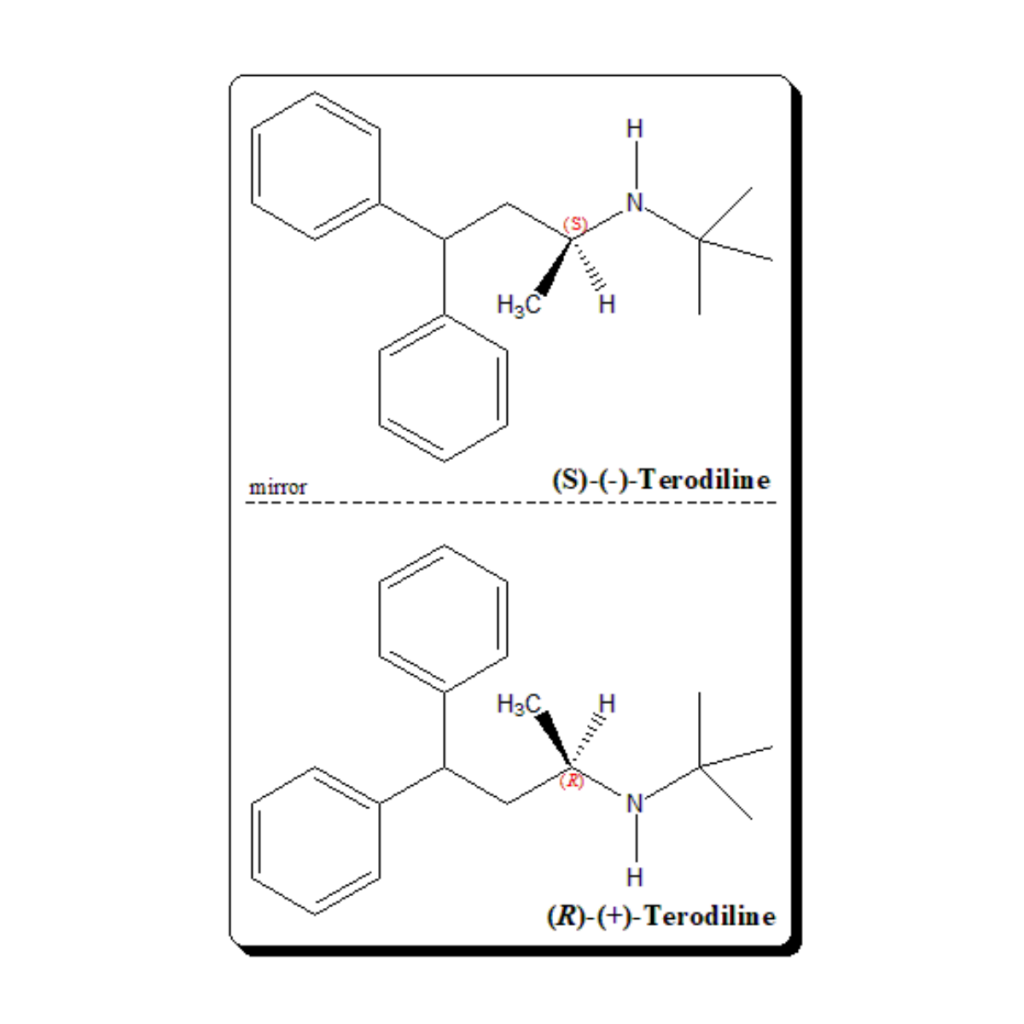
Levamisole
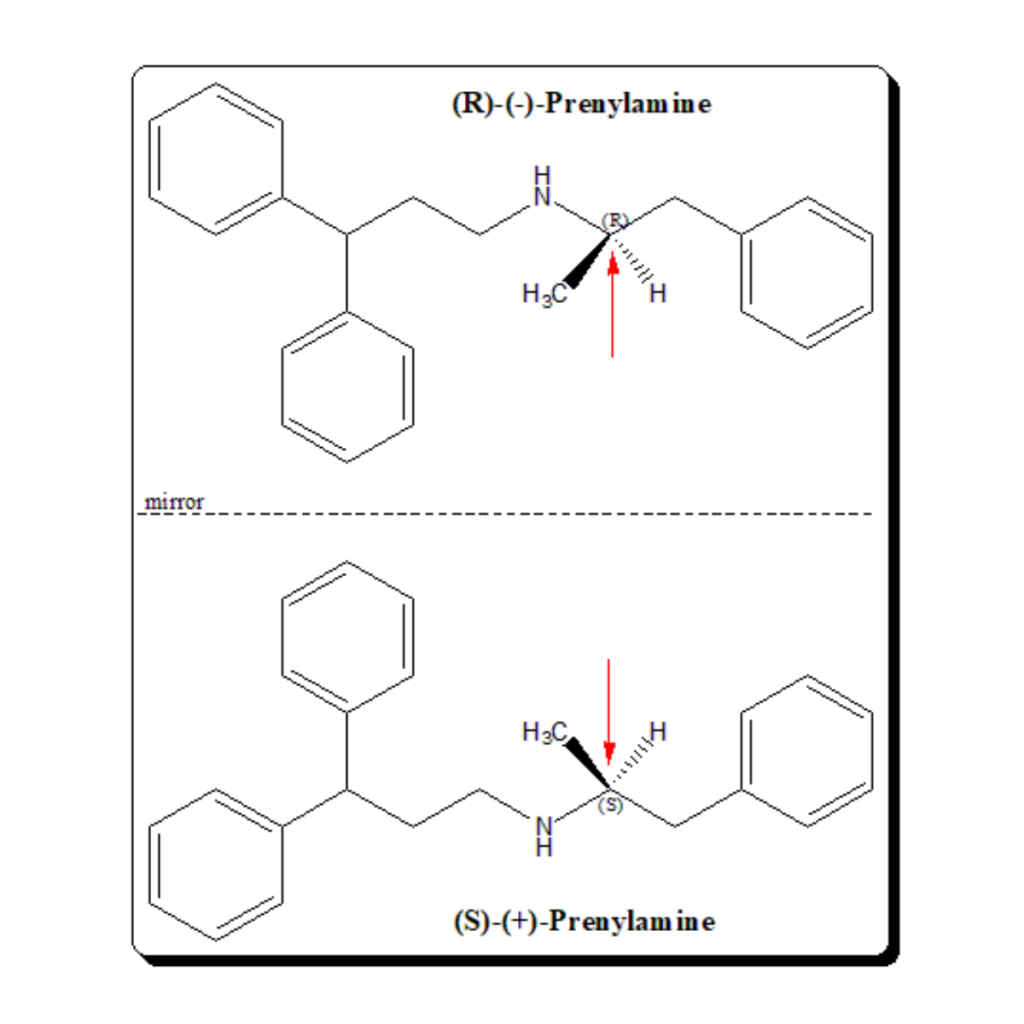
Levamisole is used as anthelmintic agent to get rid of the intestinal worms. It is (S)-(-)-enantiomer of tetramisole. This drug is used in veterinary to treat hookworm infections. Levamisole also finds therapeutic application in the treatment of colon cancer when given in conjunction with fluorouracil. Chirality and biological activity Tetramisole carries one chiral stereogenic center and exists as an enantiomeric pair. The anthelmintic activity resides in the (S)-(-)-enantiomer, levamisole. The (R)- isomer harbors undesirable …