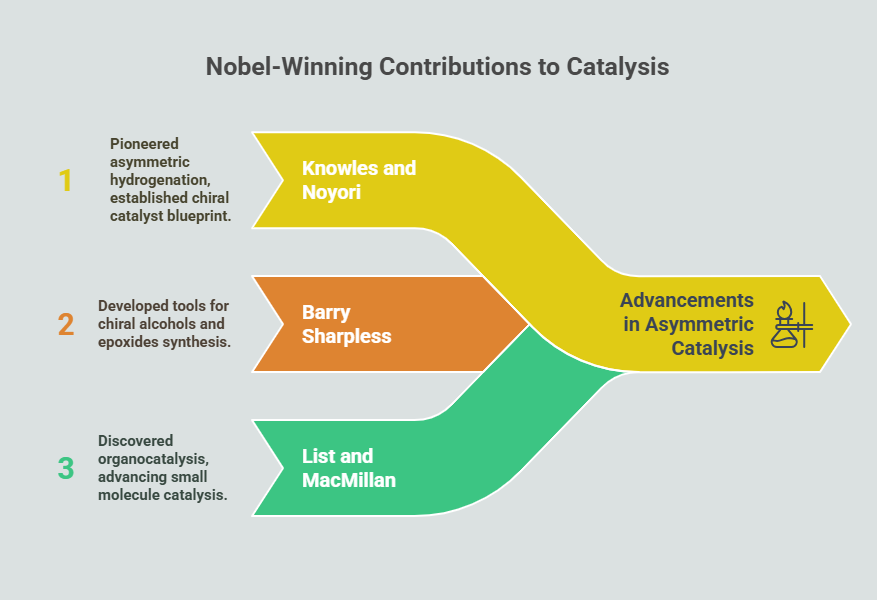
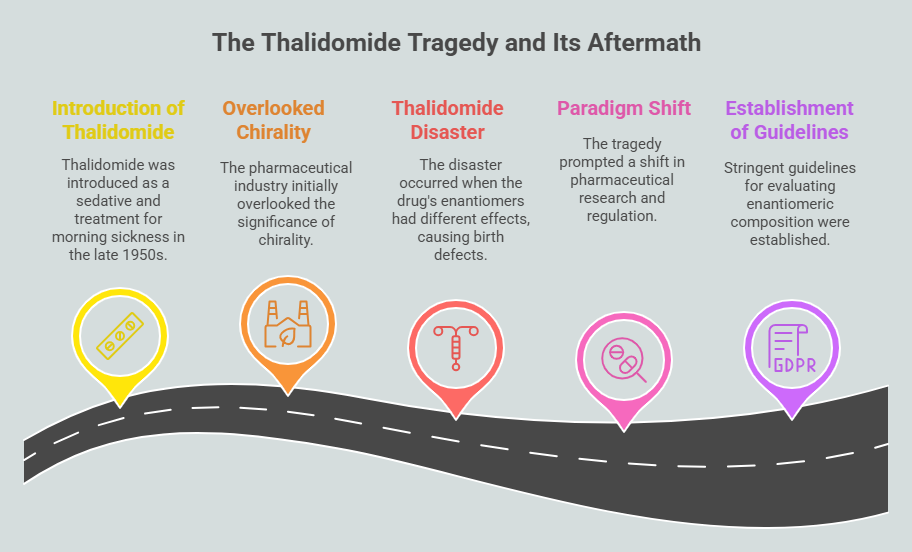
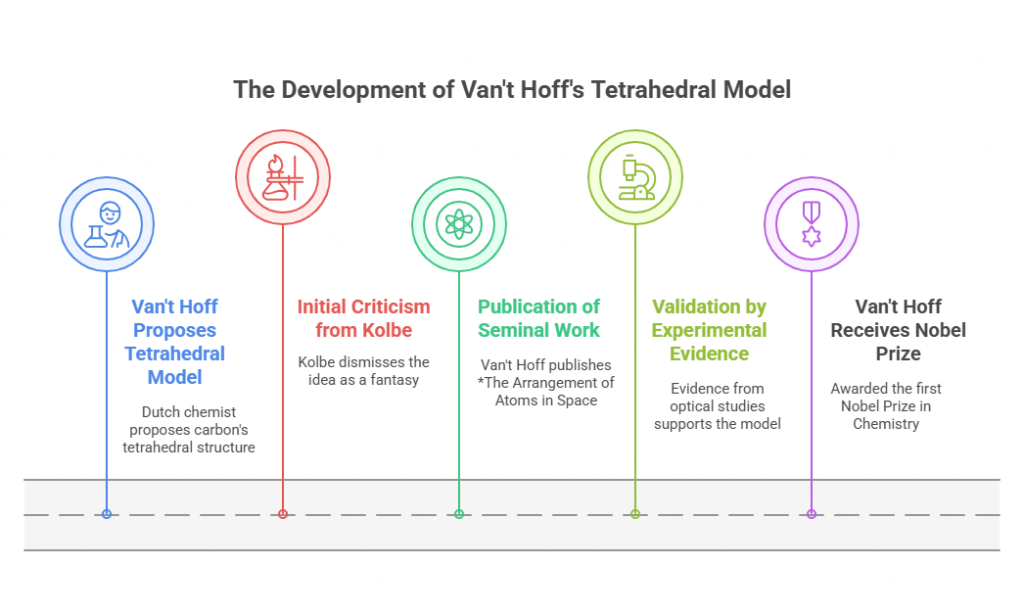
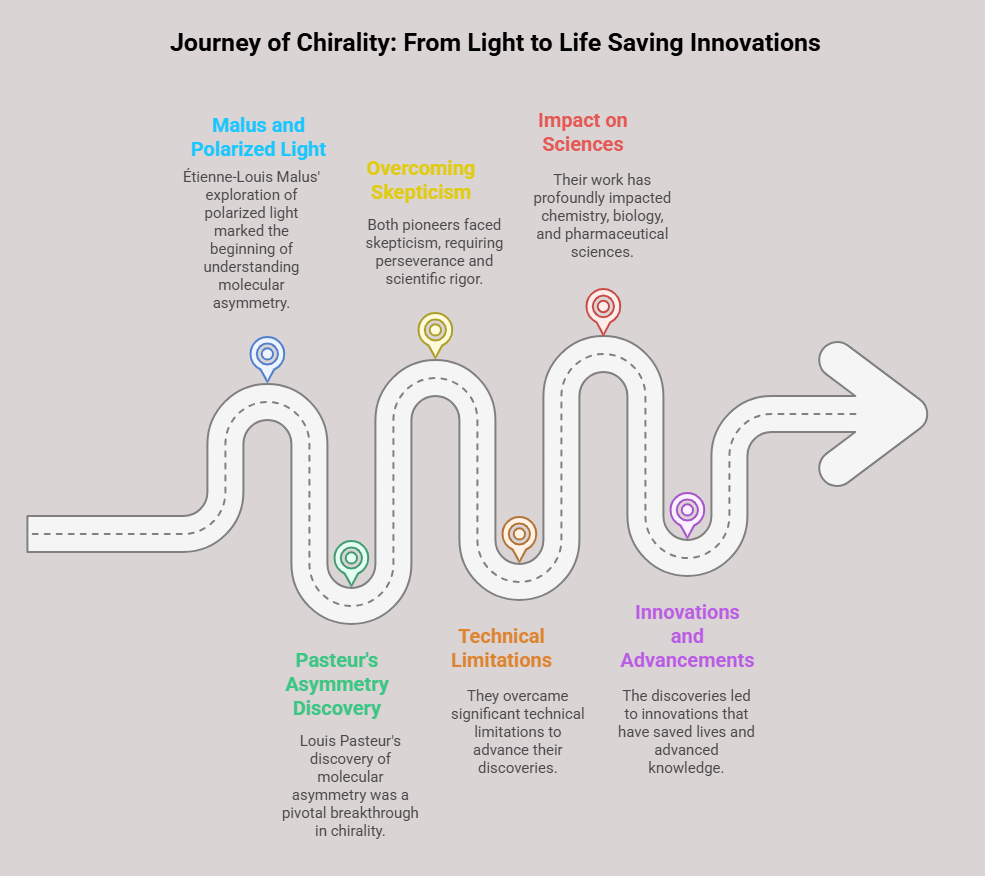
Episode 1: When Mirror Images Mattered: A Historical Prelude to Chiral Drug Regulation
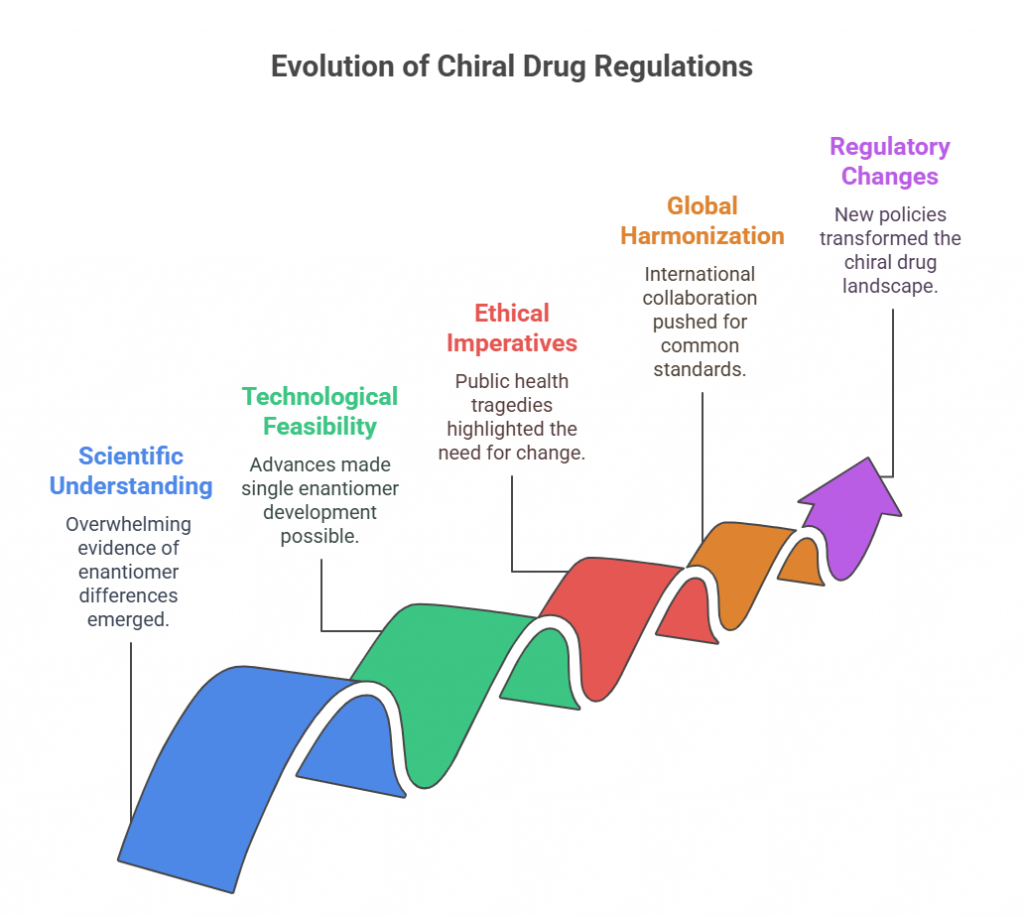
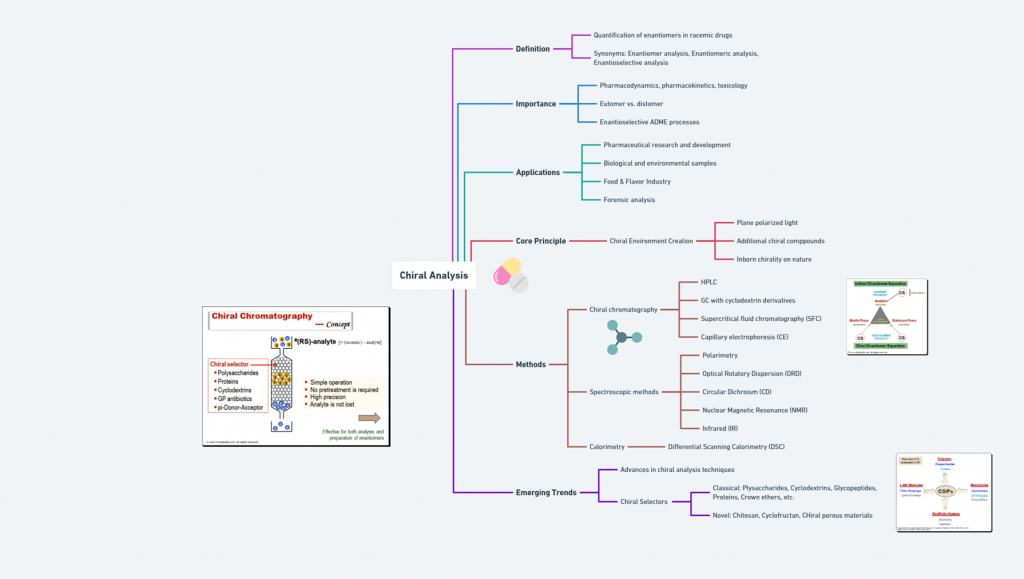
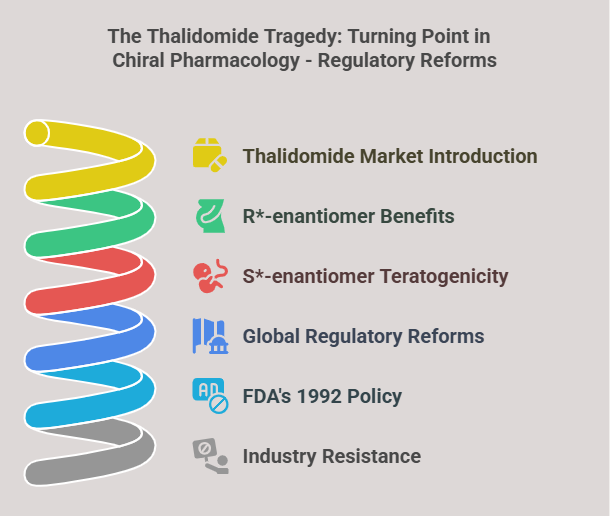
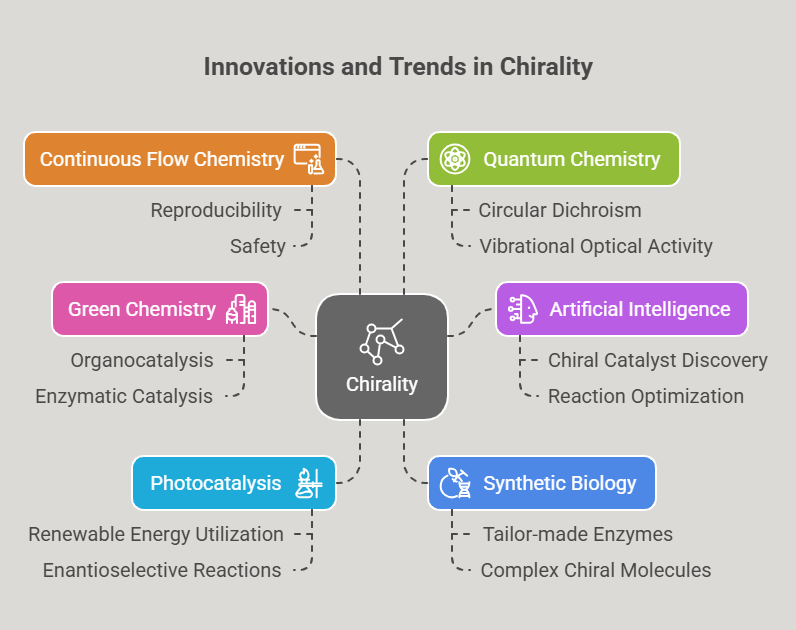
“Before the world looked closely at molecular mirror images, the pharmaceutical landscape was filled with blind spots -this is the story of how chirality found its voice.” Introduction The phenomenon of chirality, where molecules exist as non-superimposable mirror images, permeates the natural world. In biological systems, chirality is fundamental: proteins, enzymes, and receptors are inherently stereospecific, responding differently to the two mirror-image forms, or enantiomers, of a compound. In pharmacology, these subtle molecular differences can …
Episode 1: When Mirror Images Mattered: A Historical Prelude to Chiral Drug Regulation Read More »