Bupivacaine is a long acting local anesthetic in use for many years as a spinal/epidural anesthetic for childbirth and orthopedic procedures, such as hip replacement. It is marketed by AstraZeneca under the trade name Chirocaine. It acts by blocking Na+ channels and also has actions on the heart, which restrict its use by intravenous injection for regional anesthesia.
Chirality and Biological activity
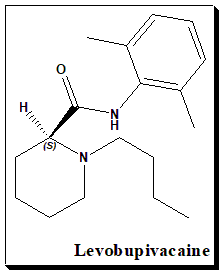
Bupivacaine is a racemic drug. This an example where the distomer shows toxic effect and the need for a switch. The chiral switch of (±)-bupivacaine, , (S)-(–)-enantiomer levobupivacaine, has been developed successfully as a safer local anaesthetic that has the same therapeutic indications as the racemate. Levobupivacaine exhibits less vasodilation and possesses a greater length of action in comparison to bupivacaine. R-Bupivacaine, the distomer, has a greater risk of cardiotoxicity.
Claims justifying the switch
- Levobupivacaine has decreased risk of cardiotoxicity than the R-form and the racemate
- Other clinical profiles are essentially similar as the racemate.
Nomenclature
(2S)-1-butyl-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)piperidine-2-carboxamide
Exercise
Number levobupivacaine heterocyclic ring system. Understand the sterostructure. Look for alternate systematic names.
References
Chiral switch. Wikipedia, Wikipedia Foundation, 080/08/2022. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chiral_switch and references therein
Israel Agranat, Hava Caner and John Caldwell, Nature reviews, Drug Discovery, 1, October,| 753-768, 2002.