Salbutamol (also known as Albuterol ) is used to prevent and treat wheezing and shortness of breath caused by breathing problems (such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease). Salbutamol is a short-acting, selective beta2-adrenergic receptor agonist used in the treatment of asthma and Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Synonym
Albuterol
Chirality and biological activity
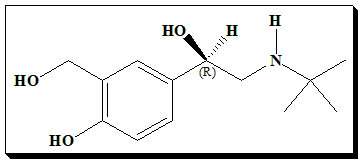
Salbutamol is formulated as a racemic mixture of the R- and S-isomers. Bronchodilator activity resides in R-(-)-Salbutamol (eutomer); S-Salbutamol (distomer) is inactive. The active (R)-enantiomer undergoes significantly faster metabolism than the inactive (S)-(+)-enantiomer after oral administration. Distomer is cleared more slowly and hence tends to accumulate in preference to eutomer. These pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic differences provided the basis for chiral switch of salbutamol to levosalbutamol. To know more about eutomer and distomer nomenclature read @ <https://chiralpedia.com/blog/chiral-twins-identical-but-not-really/>
Claim for the chiral switch from Salbutamol to Levosalbutamol
- Decreased development of airways hyper-reactivity.
- Superior side-effect profile compared to rac-salbutamol
These lead to the development of levosalbutamol, the single R-isomer of salbutamol.
Nomenclature
(R)-1-(4-Hydroxy-3-hydroxymethylphenyl)-2-(ter-butylamino)ethanol
Therapeutic category
Bronchodilator
References
Chiral switch. Wikipedia, Wikipedia Foundation, 30/07/2022. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chiral_switch
Kathryn Blake and Hengameh Raissy. Pediatric allergy, immunology, and pulmonology, 26, 3, 157-60, 2013
Harkishan Singh and V.K. Kapoor. Medicinal chemistry and pharmaceutical chemistry, Vallabh Prakashan, New Delhi, Page 209-10, 2012.