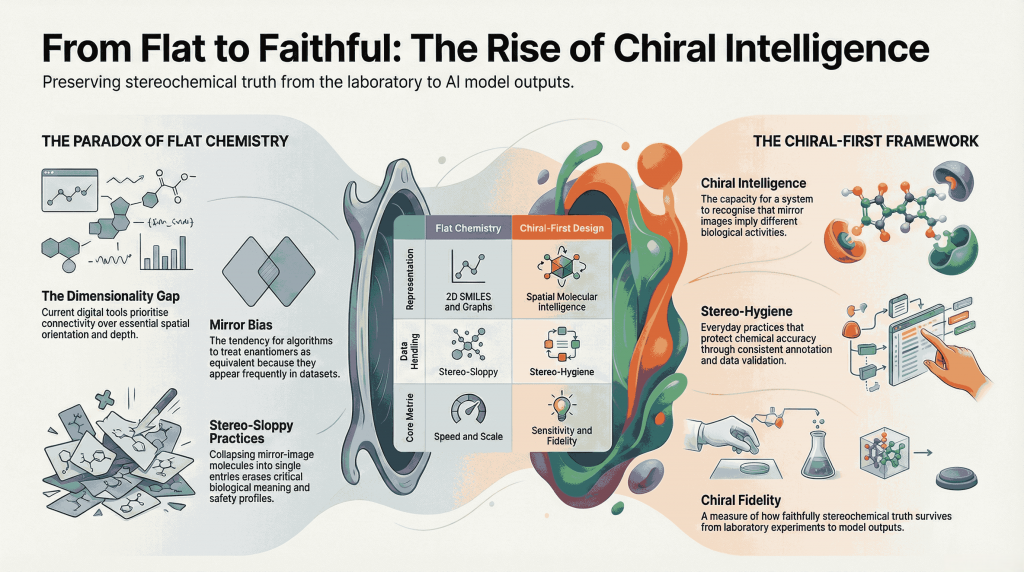
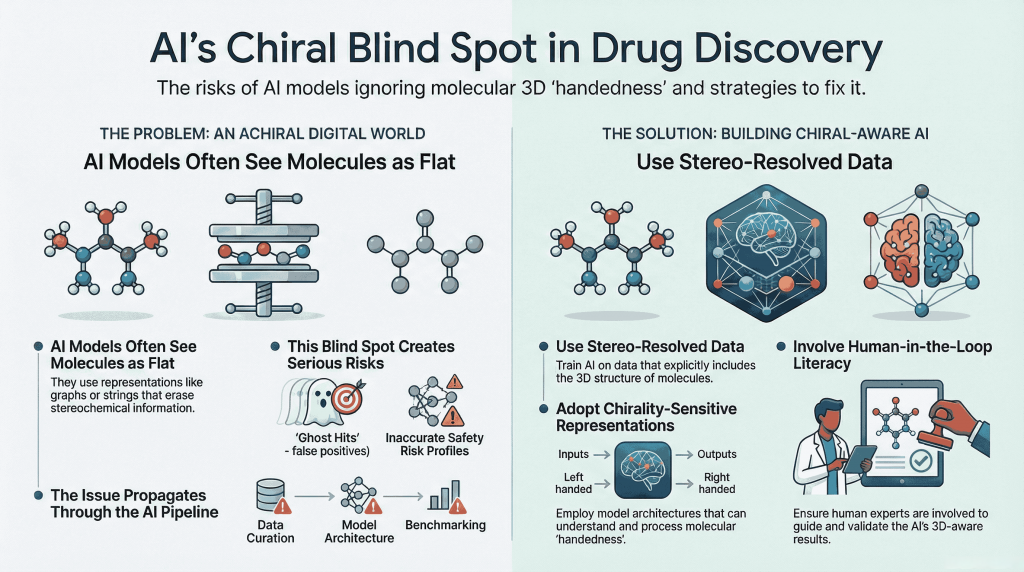
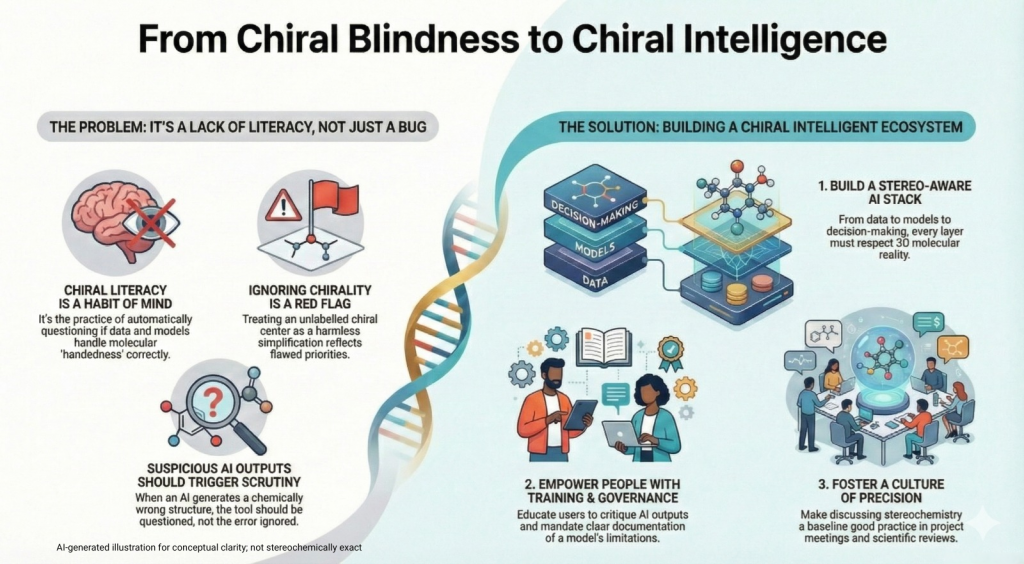
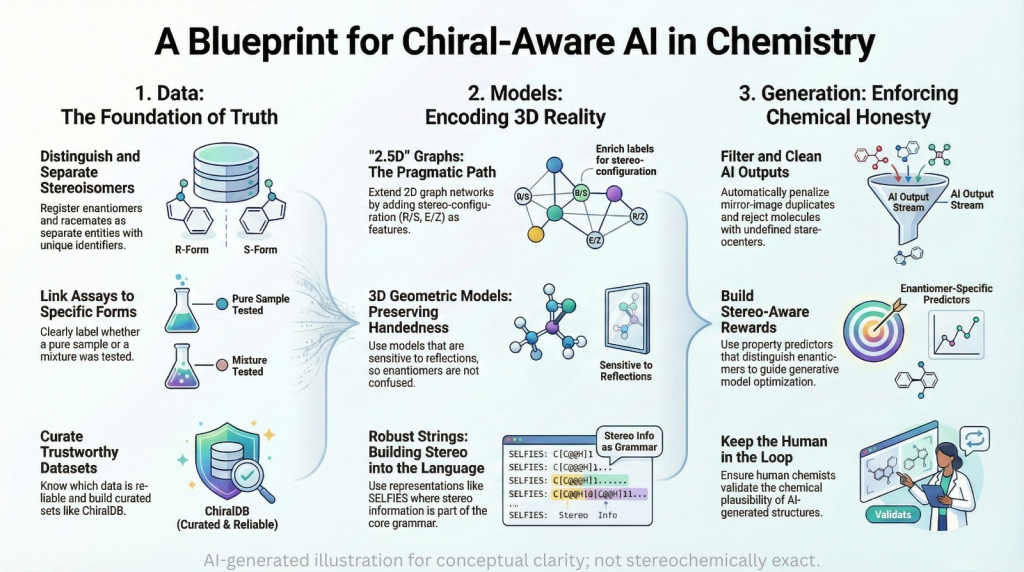
🚨🪞Mirror Life: When Chirality Flips, Does Biology Unravel?🧬🌍
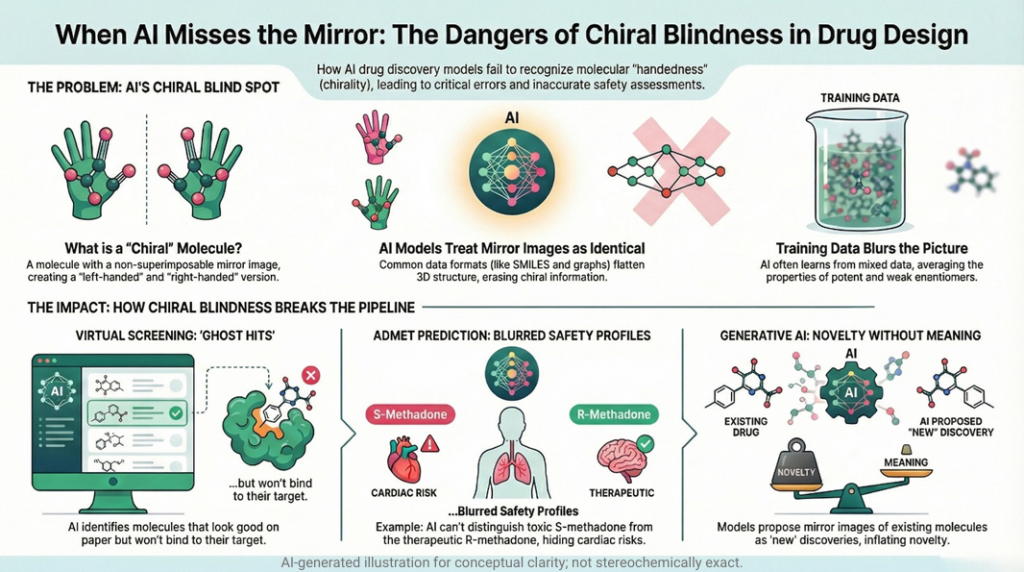
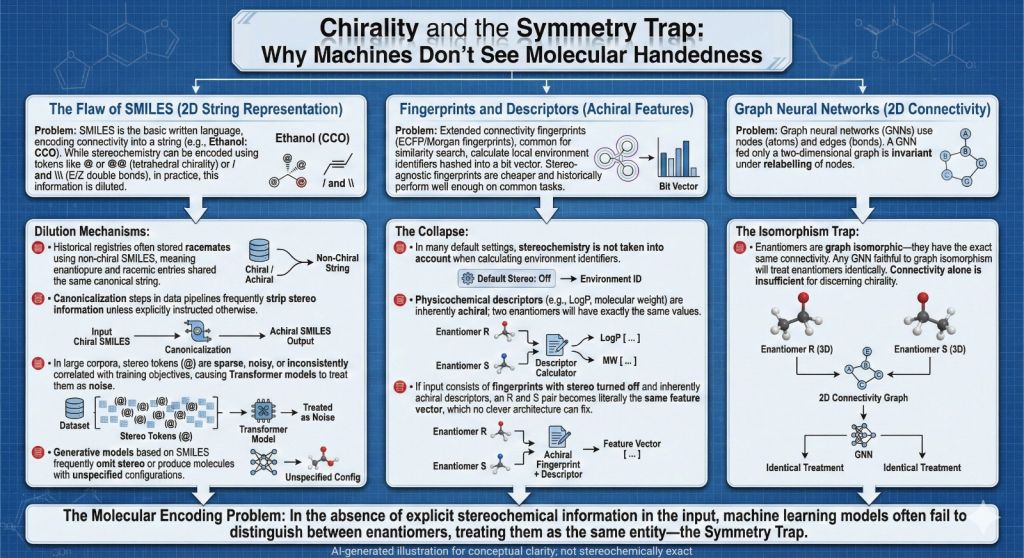
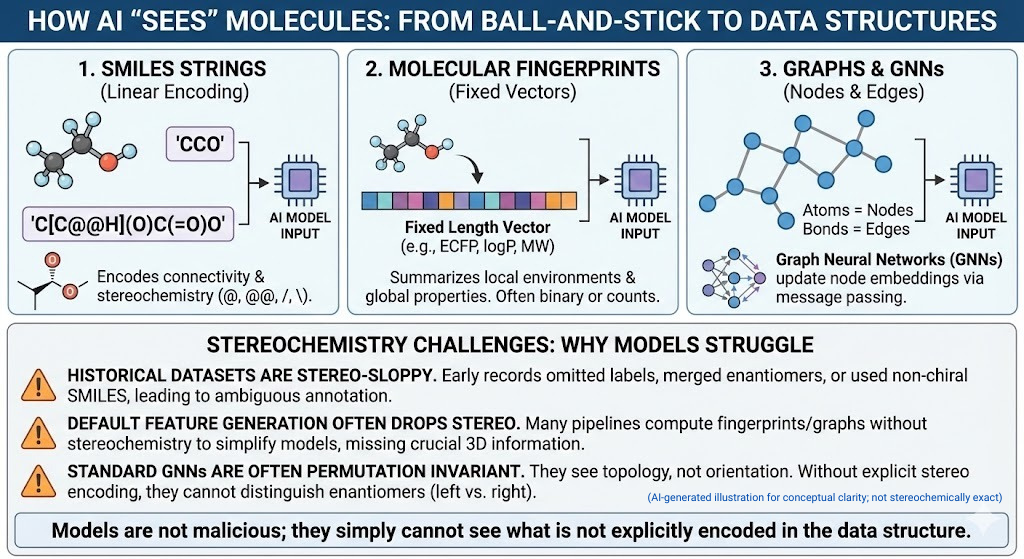
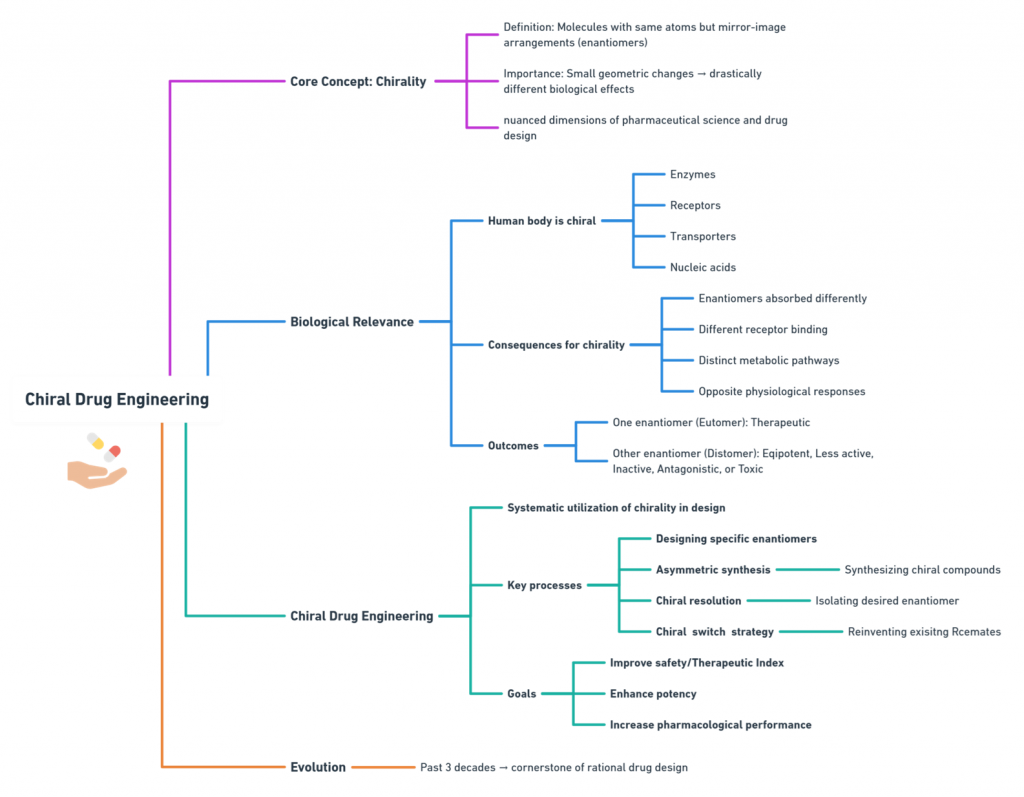
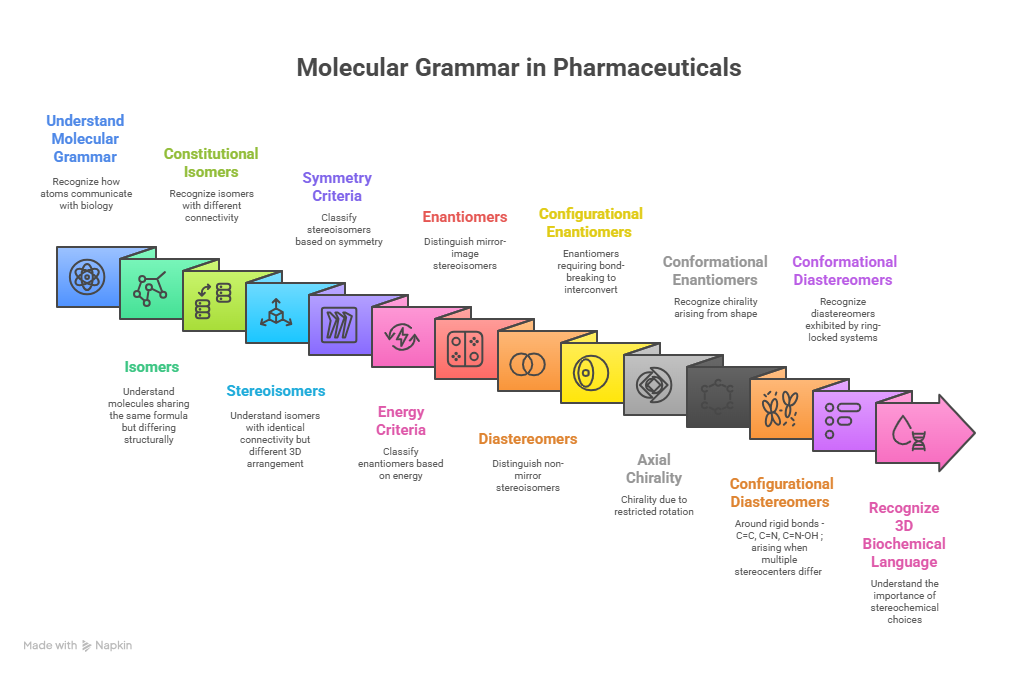
The Mirror We Build Defines the World We Keep; Decoding the Science, the Risks, and the Responsibility Synopsis: Mirror Life: When Chemistry Meets Philosophy Recently, Scientific American published two striking pieces that push chemistry into almost philosophical territory: Both ask a radical question: what if we rebuilt life itself using mirror‑image molecules? For decades, chirality—the “handedness” of molecules—has been the quiet backbone of medicinal chemistry. We’ve argued over single enantiomers versus racemates, perfected stereoselective synthesis, …
🚨🪞Mirror Life: When Chirality Flips, Does Biology Unravel?🧬🌍 Read More »