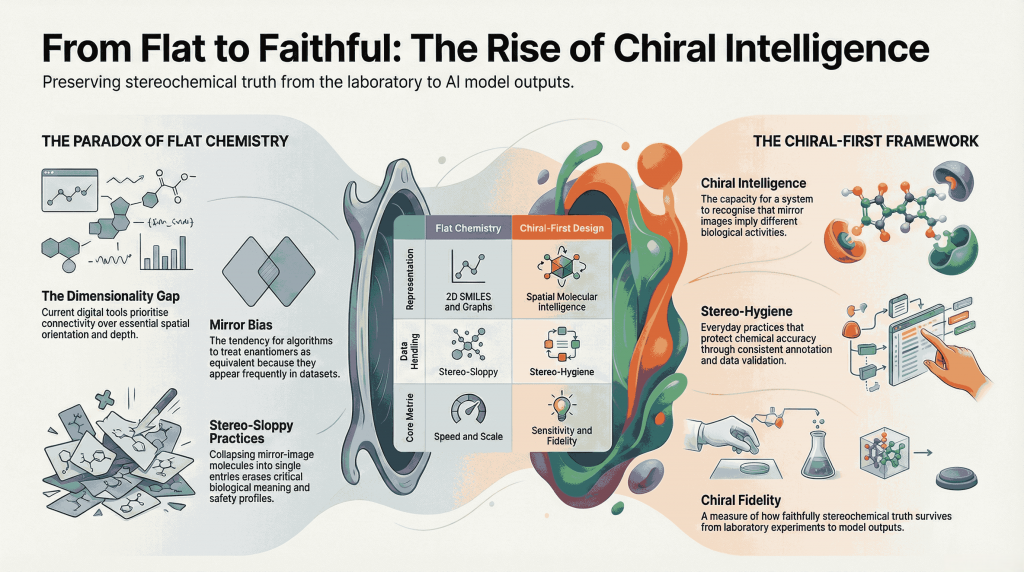
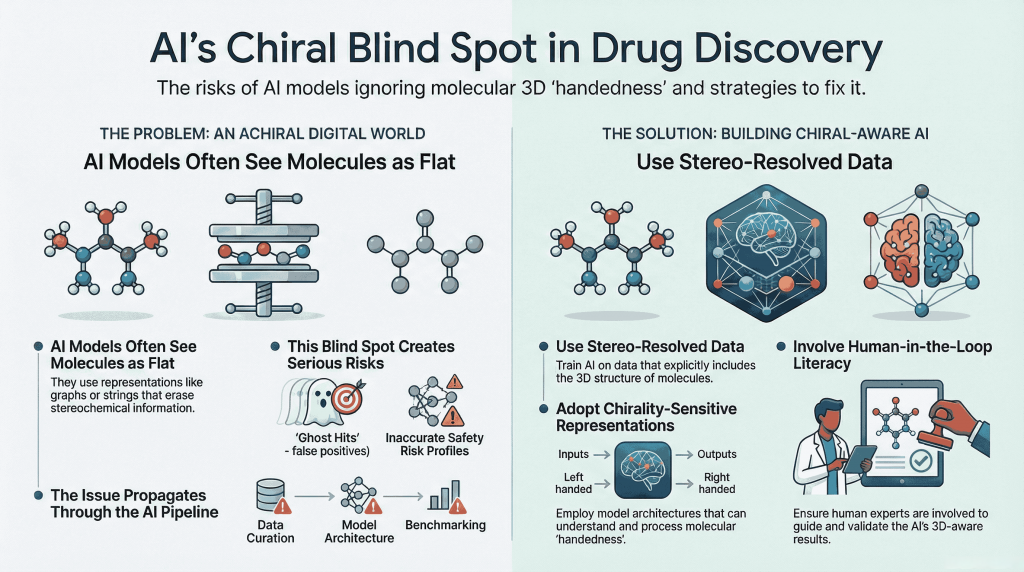
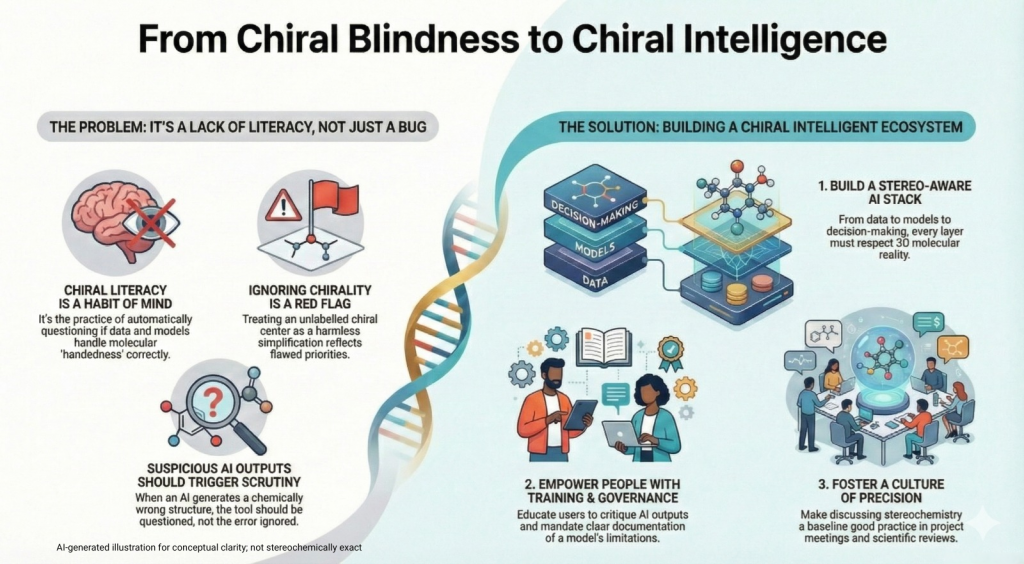
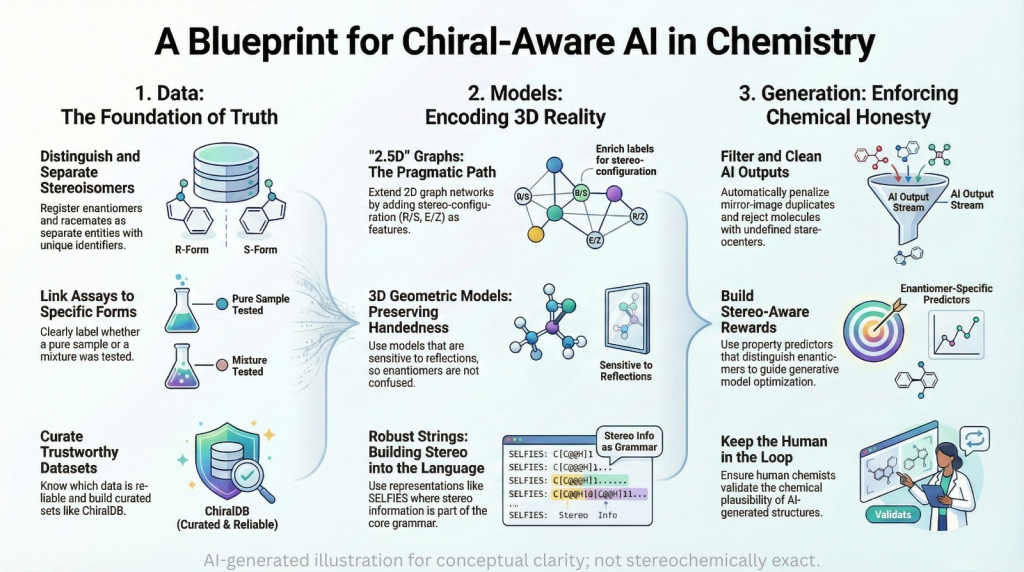
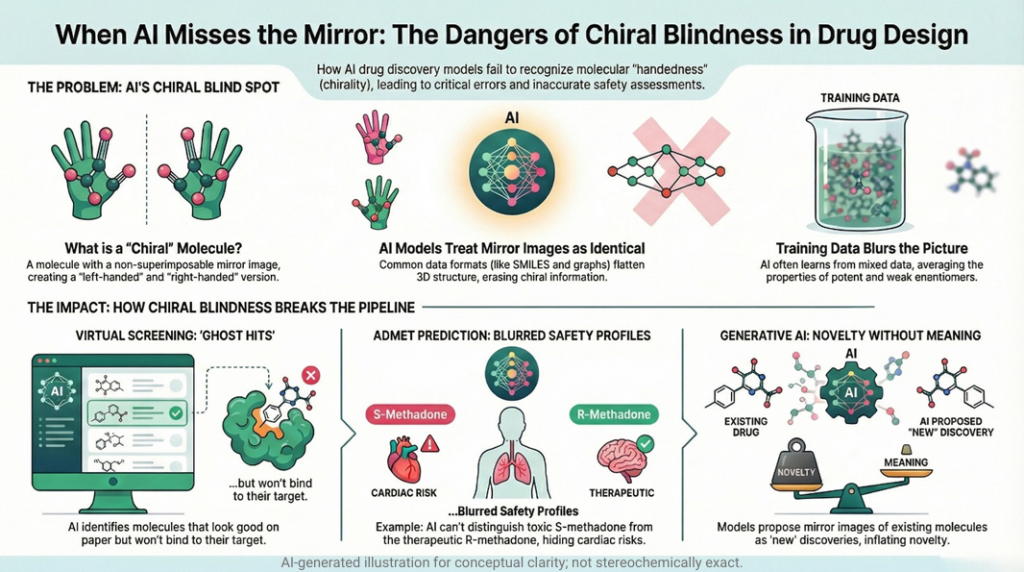
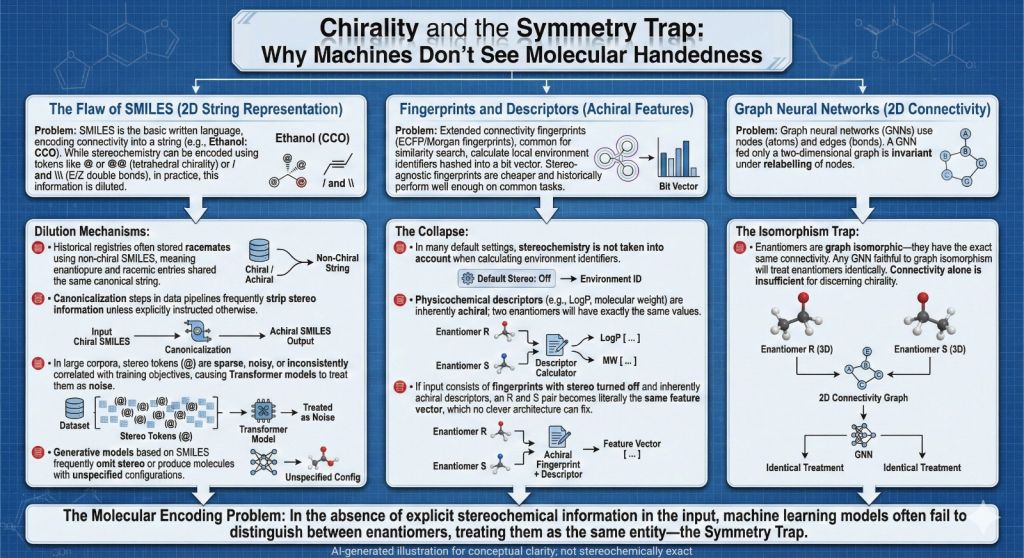
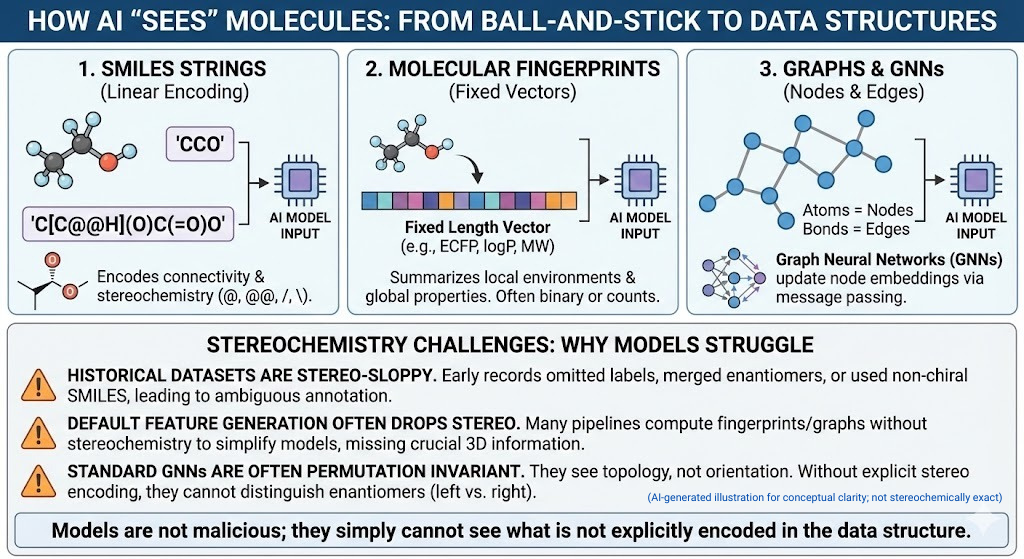
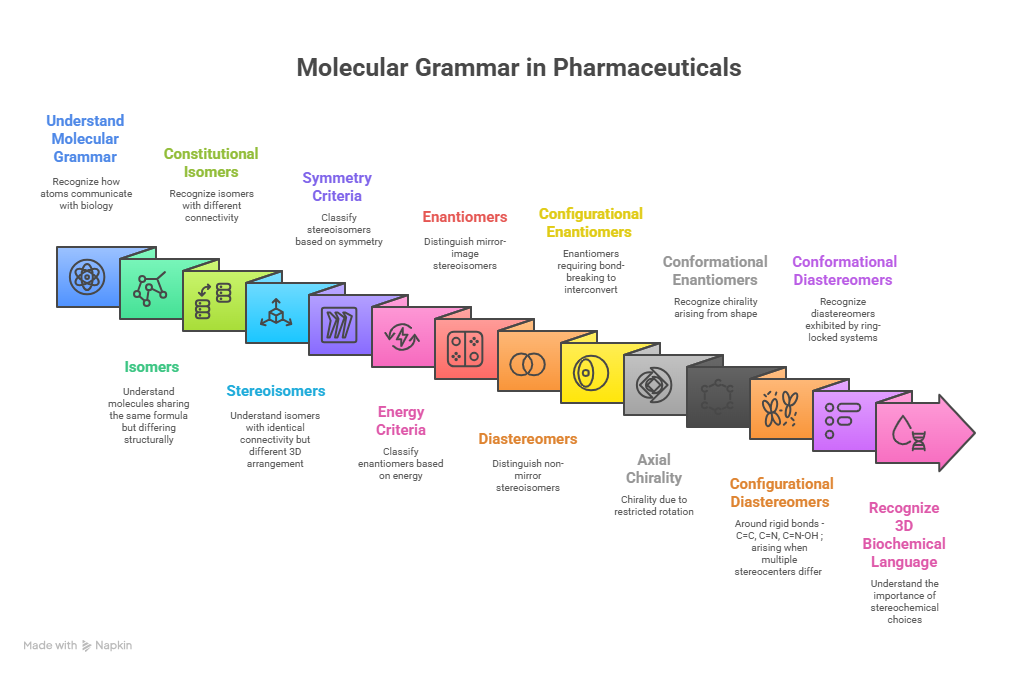
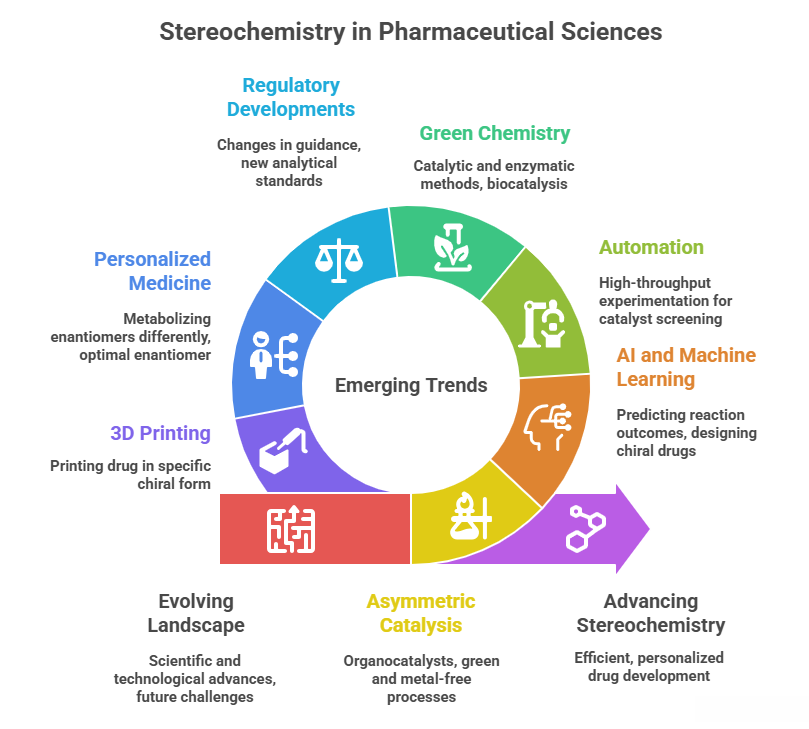
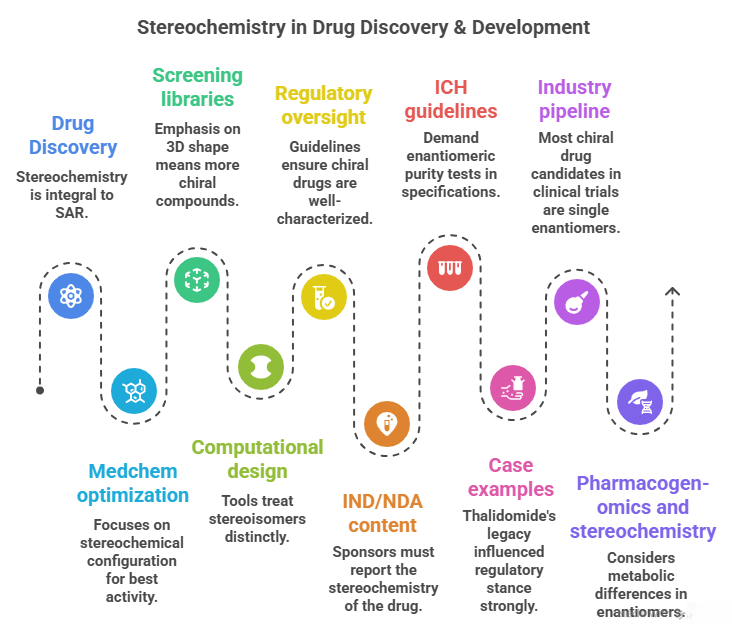
🪞Why the Language of Chirality Must Evolve: When Molecules Speak in 3D and Models Listen in 2D🤖
A chiral perspective on how we describe, teach, and encode molecular handedness in the age of artificial intelligence Prelude Chiral molecules are not flat drawings on paper (2D). They live in space (3D). They twist, reflect, and occupy three dimensions in ways that decide how they bind to receptors, how they are metabolized, and ultimately how they shape biological outcomes. This spatial reality—what chemists call chirality—has always been at the heart of pharmaceutical science. The …